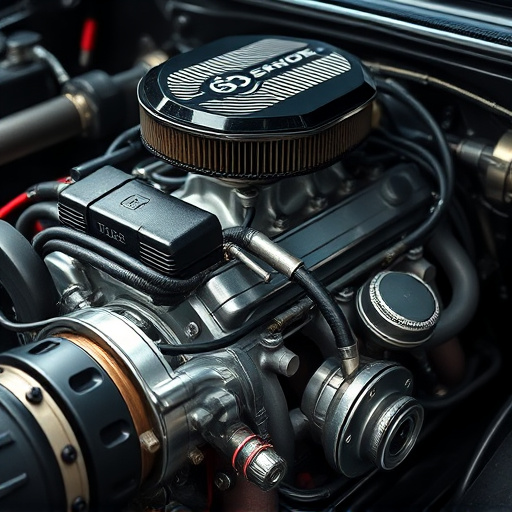
The Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor is vital for precise engine combustion, sending data to the ECU for fuel injection. Regular maintenance prevents contamination from dust or debris. Upgrades like cold air intakes can highlight MAF sensor issues. Malfunctions cause decreased performance, increased fuel consumption, and potential damage; immediate replacement is advised. Diagnosing involves OBD-II scans and visual inspections.
In modern vehicles, the mass air flow (MAF) sensor plays a vital role in maintaining optimal engine performance. This critical component measures the volume of air entering the engine, ensuring fuel-air mixture accuracy. However, over time, the MAF sensor can exhibit common symptoms of failure, leading to poor engine performance and increased emissions. This article delves into the basics of the MAF sensor, reveals typical malfunctions, and guides readers through diagnosis and replacement processes for a faulty sensor, empowering DIY enthusiasts with essential knowledge.
- Understanding Mass Air Flow Sensor Basics
- Common Failures and Malfunctions Revealed
- Diagnosing and Replacing the Faulty Sensor
Understanding Mass Air Flow Sensor Basics

The Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor is a crucial component in your vehicle’s engine management system. It plays a vital role by measuring the mass flow rate of air entering the engine, providing critical data to ensure optimal fuel-air mixture for efficient combustion. This sensor is located in the intake air stream, often near the air filter, and is directly connected to the engine control unit (ECU). The MAF sensor’s primary function is to convert the volume of air into a mass measurement, which is essential for precise fuel injection.
Regularly maintaining your MAF sensor is key to preventing common issues. Over time, it can become contaminated by dust, debris, or oil residue from the air filter kits, affecting its accuracy. Upgrading to high-quality cold air intakes or installing visible exhaust tips can help keep the sensor clean and functioning optimally. Understanding the basics of this component empowers vehicle owners to identify potential problems early on, ensuring smooth engine performance and preventing costly repairs.
Common Failures and Malfunctions Revealed

The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is a vital component in your vehicle’s engine management system. When this sensor fails or malfunctions, it can manifest through several common symptoms. One of the most noticeable signs is a decrease in engine performance, often characterized by a lag or loss of power when accelerating. This occurs because the MAF sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine and sends this data to the engine control unit (ECU), which adjusts fuel injection accordingly. A faulty sensor can provide inaccurate readings, leading to an incorrect fuel-air mixture.
Additionally, irregular idling, stalling, or rough running of the engine are red flags. If your vehicle’s brake pads need frequent replacement, it could be linked to a malfunctioning MAF sensor, as under-air (or rich) mixtures can cause excessive fuel consumption and increased wear on various components, including brake pads and catalytic converters. Even modifications like cold air intakes or aftermarket air intake systems may highlight issues with the MAF sensor, as these changes disrupt the natural airflow, exacerbating any existing sensor problems.
Diagnosing and Replacing the Faulty Sensor

If your vehicle is showing signs of a faulty mass air flow (MAF) sensor, it’s crucial to address the issue promptly for optimal engine performance and efficiency. Diagnosing a bad MAF sensor involves checking for unusual behaviors from your car, such as reduced fuel efficiency or poor engine power. An OBD-II scanner can detect error codes related to the sensor, guiding you towards further testing. Physically inspecting the sensor is also beneficial; look for signs of damage, corrosion, or debris buildup.
Replacing a faulty MAF sensor requires a few key steps. Start by unplugging the sensor from its connector and removing it from the engine bay using appropriate tools. Ensure you have a replacement sensor that matches your vehicle’s specifications. Install the new sensor, reconnect it to the connector, and check for any leaks or loose connections. After replacing the sensor, consider other components like exhaust mufflers and brake rotors, as they may also be affected by previous issues or require maintenance as part of an overall vehicle health check-up.
A faulty mass air flow (MAF) sensor can significantly impact your vehicle’s performance and efficiency. By understanding common symptoms like reduced fuel efficiency, poor engine performance, and check engine lights, you can proactively address issues. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of the MAF sensor are key to keeping your vehicle running smoothly. Diagnosing problems with this component is often straightforward, and a simple repair can restore optimal engine operation.