Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensors are vital for engine management, controlling incoming airflow to optimize combustion. OEM MAF sensors provide precision and reliability, seamlessly integrating into vehicles' systems. Aftermarket sensors offer performance improvements, durability, and tuning potential at a lower cost but may face compatibility issues. Aftermarket MAF sensors have advanced technologically, sometimes surpassing OEM accuracy and durability. The choice between them depends on individual preferences: OEM for reliable compatibility or aftermarket for customization and enhanced engine performance.
Mass air flow (MAF) sensors are critical components in modern vehicles, ensuring optimal engine performance and emissions control. This article guides you through the essential differences between Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) and aftermarket MAF sensors, helping you make an informed choice. We’ll explore the basics of these sensors, their compatibility challenges, and performance implications to ensure your vehicle’s health and efficiency.
- Understanding Mass Air Flow Sensors: The Basics
- OEM vs Aftermarket: Key Differences & Compatibility
- Performance and Reliability: Making Your Choice
Understanding Mass Air Flow Sensors: The Basics

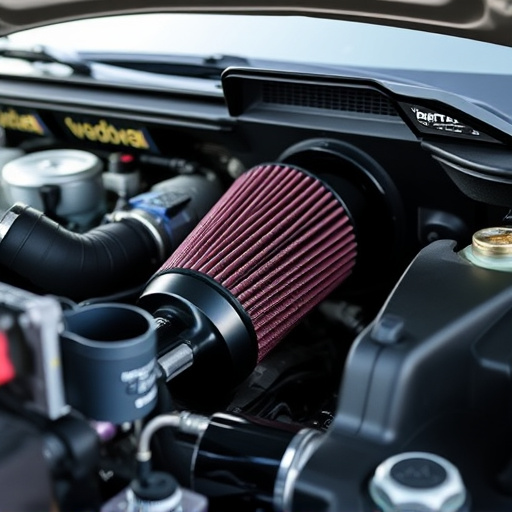
Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensors are a crucial component in modern vehicles’ engine management systems. They play a vital role in monitoring and controlling the amount of air entering the engine, which is essential for optimal combustion. The MAF sensor measures the mass flow rate of air passing through it and sends this data to the engine control unit (ECU). This information helps regulate fuel injection, ensuring the engine runs efficiently and smoothly.
These sensors are typically located in the air intake system, near the turbocharger or supercharger (if equipped), or directly in the air stream. They can be original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts, installed during the vehicle’s initial production, or aftermarket replacements, fitted later to enhance performance or replace faulty components. Aftermarket MAF sensors, often referred to as replacement parts, cater to various needs, from improving engine performance to offering more durable suspension components, while also potentially providing a unique tuning potential for car enthusiasts, who may customize exhaust tips and air intake systems accordingly.
OEM vs Aftermarket: Key Differences & Compatibility

When comparing OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) and aftermarket mass air flow sensors, understanding key differences is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in your vehicle’s engine management system. OEM sensors are designed and manufactured by the same companies that produce the vehicle or its components, often utilizing proprietary technology and exacting specifications. They’re known for their precision, reliability, and seamless integration into the car’s existing systems, including air intake systems and performance brakes.
Aftermarket mass air flow sensors, on the other hand, are produced by third-party manufacturers aiming to offer more affordable alternatives. While they may be interchangeable with OEM parts in terms of physical fit, compatibility can sometimes present issues due to differences in sensor readings or communication protocols. Aftermarket sensors might not always provide the same level of accuracy as their OEM counterparts, but they’re popular choices for those looking to customize their vehicles or replace worn-out components without breaking the bank, focusing on aspects like air intake systems and brake rotors.
Performance and Reliability: Making Your Choice

When comparing OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) and aftermarket mass air flow sensors, performance and reliability are paramount. Aftermarket sensors have made significant strides in technology, often offering enhanced accuracy and durability compared to their OEM counterparts. These improvements can lead to better fuel efficiency, improved engine performance, and reduced emissions—all crucial factors for those looking to optimize their vehicle’s capabilities.
Choosing between the two ultimately depends on your priorities. OEM sensors are known for their reliability and compatibility with your vehicle’s specific specifications, ensuring a seamless integration. Aftermarket sensors, however, provide opportunities for customization, especially when paired with performance enhancements like suspension kits or air filter kits. They can offer fine-tuned control over engine inputs, making them attractive to those seeking that extra edge in performance exhaust systems.
When choosing between OEM and aftermarket mass air flow sensors, understanding their distinct characteristics is key. While OEM sensors offer superior compatibility and reliability, aftermarket alternatives provide enhanced performance at a more affordable cost. Ultimately, the decision depends on your vehicle’s specific needs and budget considerations. By weighing these factors, you can ensure your car receives accurate airflow measurements for optimal engine performance.